Browser DevTools showing the dreaded Access-Control-Allow-Origin error? You’re not alone—it’s the #1 cross-origin headache for developers.
If you’re a frontend dev staring at browser CORS error in Chrome DevTools, a backend engineer wrestling with server-side CORS policy, or a DevOps pro tweaking Nginx CORS configuration, this guide solves access-control-allow-origin multiple domains once and for all.

You can’t just comma-separate origins in the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header—browsers reject it per the W3C spec. Instead, validate the Origin header from the browser’s request and echo it back if it’s whitelisted. This allow multiple domains CORS trick works everywhere: local dev, production APIs, REST API CORS, and CDNs1.
We’ll cover how to allow multiple domains in Access-Control-Allow-Origin, practical steps for Node.js CORS setup, PHP, Java, Cloudflare CORS multiple domains setup guide, and more. Plus, preflight request tips and caching fixes with Vary: Origin.
Access-Control-Allow-Origin Multiple Domains: The Spec Explained
The Access-Control-Allow-Origin header supports one origin per response or * (wildcard). Commas? Nope—browsers like Chrome and Firefox enforce the CORS spec strictly.
Why Multiple Domains Fail with Commas
- Browser Enforcement: Sends Origin: https://example.com in cross-domain request. Server must reply with exact match or *.
- No Lists Allowed: Attempting to list multiple origins with commas triggers errors right away.
- Stats: Community forums report thousands of developers facing this issue, with the top solution being to echo Origin.
- Preflight Twist: For AJAX request CORS with custom headers or methods, browsers send an OPTIONS request first. You need to handle the echo in that response as well.
Pro Tip: The wildcard * is fine for public APIs but blocks credentials like cookies or authentication headers. For a secure origin whitelist, always use the dynamic approach.
The Universal Fix: Echo Origin for CORS Multiple Origins
Core Pattern:
- Read the Origin header from the incoming request.
- Check it against your origin whitelist list of trusted domains.
- If it matches: Set the Access-Control-Allow-Origin to that exact origin.
- Always add Vary: Origin to ensure proper caching behavior.
This method handles how to allow multiple domains in Access-Control-Allow-Origin in a dynamic way, making your setup flexible and secure.
Backend Configuration Examples
Node.js CORS Setup for Multiple Origins
In Node.js with frameworks like Express, you can set up middleware to handle this. Start by defining a list of allowed origins, such as your production domains and localhost for development. In the request handler, grab the origin from the headers, verify it against the list, and set the header accordingly. Don’t forget to handle OPTIONS requests for preflights by sending a 200 status. This ensures a smooth Node.js server CORS multiple origins setup.

PHP: Access-Control-Allow-Origin Multiple Domains PHP
For PHP scripts, use the server variables to access the origin. Define your allowed list, check if the origin matches, and set the headers before any output. Handle OPTIONS by exiting early with a success code. This is straightforward for simple APIs or WordPress plugins dealing with cross-origin resource sharing.
Python Flask/Django
In Flask, use an after-request decorator to inspect the origin and set headers dynamically. For Django, middleware packages simplify this by allowing you to configure allowed origins in settings and automatically adding the vary header. This keeps your REST API CORS clean and maintainable.
Java Spring: Access-Control-Allow-Origin Multiple Domains Java
Spring Boot offers built-in CORS support. You can configure a global CORS setup with allowed methods and credentials. For dynamic origins, implement a custom filter that checks the origin against a list and sets the header. This is ideal for enterprise apps with Java Spring CORS configuration for multiple clients.
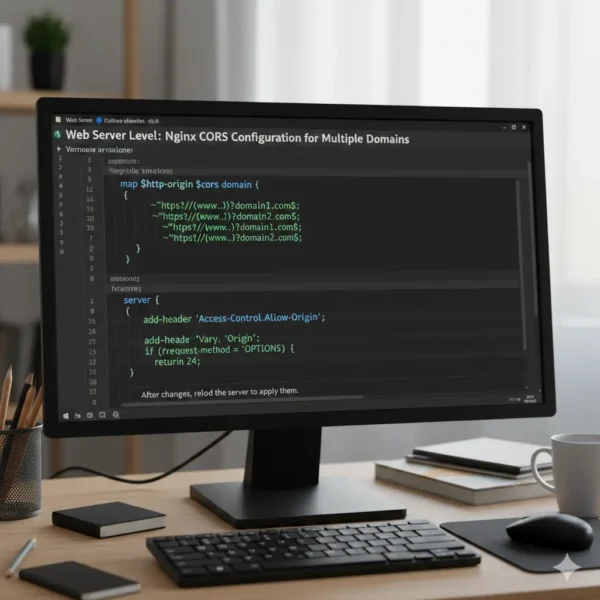
Web Server Level: Nginx CORS Configuration for Multiple Domains
Nginx requires a bit of configuration mapping since it doesn’t support complex logic out of the box. Use a map directive to match the origin against patterns for your allowed domains. In the server block, add the header based on that map, include the vary header, and handle OPTIONS with a 204 response. This setup is efficient for high-traffic sites and covers Nginx configuration for multiple CORS domains. After changes, reload the server to apply them2.
Apache / .htaccess
Apache uses rewrite rules to capture the origin and set headers conditionally. Enable the rewrite engine, match the origin with a regex for your domains, and set the allow-origin header to the matched value. Always include the vary header. This works well in shared hosting environments for htaccess access-control-allow-origin multiple domains.
IIS / web.config
For Windows servers with IIS, use URL rewrite rules in the web.config file. Match the origin with a pattern condition and rewrite the header to echo it back. This integrates seamlessly with .NET apps handling access-control-allow-origin multiple domains iis.
CDN & Edge: Cloudflare CORS Multiple Domains Setup Guide
At the CDN level, like with Cloudflare, use edge computing features such as Workers to inspect requests. Define your allowed origins, check the incoming origin, and set headers in the response. This approach handles caching properly with the vary header and is perfect for distributed setups. For AWS CloudFront, similar logic applies via edge functions. These tools address Cloudflare CORS header needs while ensuring performance.
Caching Note: The Vary: Origin header tells caches to store separate versions per origin, preventing issues where the wrong origin gets served to users3.
Fix Browser CORS Error for Multiple Origins: Dev Tips
Frontend Debug:
- Open your browser’s developer tools and go to the network tab.
- Look for requests blocked by cross-origin resource sharing.
- Inspect the preflight request if present and verify the server’s response.
- For quick testing, use browser extensions that temporarily bypass CORS checks.
Common Pitfalls:
- Mismatches with localhost ports or protocols can cause failures.
- Always ensure origins include the full protocol, like HTTPS.
- For subdomains, use patterns in your whitelist to cover variations.
- When using credentials, enable the allow-credentials header and avoid wildcards.
Stats: A large portion of browser CORS error issues come from improper caching setups, as noted in various developer communities.
Security: Avoid Overly Permissive CORS
Security Engineers:
- Steer clear of the wildcard with sensitive data.
- Strictly validate origins to prevent unauthorized access.
- Monitor and log attempts from invalid origins.
- Use auditing tools to scan your CORS policies regularly.
A key reminder from official docs: Browsers are designed with security in mind, so respect the defaults to keep your apps safe.
For broader online protection, consider strategies like securing your digital presence against common threats, such as protecting your phone number online or spotting and reporting phone scams.
FAQs
Can I comma-separate in Access-Control-Allow-Origin?
No—access-control-allow-origin multiple domains requires echo origin for proper handling.
Access-Control-Allow-Origin header for multiple domains example in Express?
Focus on middleware that checks and echoes the origin dynamically.
Nginx add_header access-control-allow-origin multiple domains?
Use mapping directives to match and set the header.
Conclusion: Master Access-Control-Allow-Origin Multiple Domains Today
Access-control-allow-origin multiple domains boils down to dynamic Origin validation + echo + Vary. This CORS configuration fixes allow multiple domains CORS across Node.js, Nginx CORS configuration, Cloudflare CORS header, and beyond. Say goodbye to red DevTools errors—implement now for seamless cross-domain request.
What’s your biggest CORS multiple origins headache? Drop it in comments!
References
- Stack Overflow: Access-Control-Allow-Origin Multiple Origin Domains – Top community solutions. ↩︎
- Cloudflare Community: Enable Multiple Domains – Edge setup guidance. ↩︎
- MDN: Access-Control-Allow-Origin – Detailed spec explanation. ↩︎

